From fat droplets in plant cells to novel foodsFunctional nanoparticles - von Dr Birgitta Zielbauer, Prof. Behic Mert, Prof. Thomas Vilgis
Occurring naturally in oilseeds, oleosomes are particles with special properties. Depending on the plant variety, their size ranges from microns down into the nanoscale. These particles, with their protein-functionalized surfaces, are structurally very stable indeed. This makes them relevant for fundamental research and pharmacology, and also for innovative applications in food science.
 Cell experiments with optical tweezers are revolutionising biomedicineTweezing without touching - von Robert Meissner, Christina Alpmann, Álvaro Barroso, Prof. Dr. Cornelia Denz
Ultramodern imaging techniques such as the Nobel Prize-winning STED microscopy enable the investigation of organisms, cells, bacteria and even viruses, DNA or individual molecules at very high spatial and temporal resolution. Active intervention in these tiniest of biological structures has been largely limited to indirect methods, however. While new developments such as microtweezers and micromechanical clamps are promising, these devices generally...
 Environmental risk factorsEnvironmental risk factors and developmental windows of disease and disease prevention - von Prof. Dr. Günter Vollmer
At every stage of their life – from conception to death – organisms are exposed to a multitude of environmental factors, some of which are associated with severe health risks. Current research is now attempting to clarify the significance of particularly sensitive periods of the development of organisms, known as “developmental windows of disease”. Within these windows, there is an increased chance of specific types of changes to occur which...
 Fractionation of functional peptides with ion-exchange membrane adsorption chromatographySeparation via binding - von Prof. Dr Ulrich Kulozik, Elena Leeb
By deploying specific proteases for the enzymatic hydrolysis of proteins, the release of peptides can be controlled. This process can be used to produce functional peptides, which may exhibit an ability to reduce blood pressure or have a surface-active function. The deployment of biofunctional peptides in food as an “added value” is only possible at sufficiently effective concentrations, however. Accordingly, processes are required that...
 The critical role of fatty acid channeling between membrane and storage lipidsWhen lipid metabolism breaks down - von Prof. Dr Sepp D. Kohlwein, Dr Neha Chauhan, Dr Harald F. Hofbauer
Although as thin as the skin of a soap bubble, they are nonetheless vitally important. Biological membranes, 10,000 times thinner than a human hair, form a physiological barrier to all the cells in our body and are thus responsible for mediating exchanges between the cell interior and the external environment. Minor changes to their composition, such as those involved in lipid metabolism disorders, can have fatal consequences for events within...
 The effects of psychotherapy on DNA damage caused by traumatic stressMolecular consequences - von Dr Maria Moreno-Villanueva
The natural and social environment plays a decisive role in the life of an individual, and has significant repercussions for his or her physical and mental health. Factors in the social environment such as a high population density or noisy cities with traffic congestion and light pollution are considered to be potential stress factors. Social relationships and the working environment also exert a considerable influence on a person’s psyche...
 Cancer prevention and nutritionWhat role does epigenetics play? - von Dr Clarissa Gerhäuser
Detoxification, anti-inflammatory agents, radical scavengers, antioxi- dants, anti-hormonal effects, cell growth inhibition, programmed cell death – all are terms that have been connected with the prevention of cancer by drugs or nutritional factors over the last thirty years. For the last ten years or so, the focus has been turning to a new field: epigenetics.
 Precisely targeted regulationlab&more in conversation with Stefan Miltenyi, CEO of Miltenyi Biotec GmbH, Germany
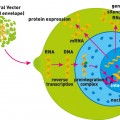
The biomedical community is euphoric about recent results in clinical trials of new treatment modalities for genetic diseases and oncological indications: T cells with modified chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) have been genetically modified with the aid of lentiviral technology and hold out the prospect of a novel form of cancer immunotherapy. Lentiviral technology itself is currently regarded as the most effective way of inserting genetic material...
 MOSH/MOAH food contaminationFocus on mineral oil residues - von Prof. Dr. Reinhard Matissek, Dr. Marion Raters, Anna Dingel, Julia Schnapka
Mineral oils are almost universally present in our environment. Their constituents can infiltrate foods of both plant and animal origin in many different ways. From the perspective of their chemical structure, the main compounds of interest are mineral oil saturated hydrocarbons (MOSH) and – to a proportionally lesser extent – mineral oil aromatic hydrocarbons (MOAH).
 Tropical pitcher plant and biomimeticsHierarchical anti-adhesive surfaces by mimiking insect traps - von Prof. Stanislav N. Gorb, Prof. Martin Steinhart
Carnivorous plants, among them tropical pitcher plants (Nepenthes spp.), have always fascinated people due to their remarkable ability to feed on animals and have constantly drawn the attention of researches as soon as new species were discovered. During past decades, different aspects of Nepenthes biology, among them the structure and functions of trapping organs (pitchers), particularly with respect to their trapping efficiency, have been the focus...
 Viruses in the waterDetection and analysis of human viral pathogens in surface waters - von Dr. Lars Jurzik, Mats Leifels
Alongside the development of methods for quantifying human viral pathogens in surface and waste waters, a key role is also played by the analysis of the resultant data. While drinking water supplies must be safeguarded on the one hand, the public must also be able to pursue waterrelated recreation activities without fearing health risks.
 Efficiency gains in day-to-day lab workInnovating with the customer - von Dr Oliver Mell
At this year's analytica, Merck Millipore's exhibition was all about the customer. The life sciences division at Merck KGaA positions itself as a strategic partner, dedicates its work as one of the three leading R&D investors for products in the life sciences industry to furthering progress in this highly forward-looking sector.
 Raman spectroscopy for biologists and cliniciansPhotons on duty for health - von Dr Karin Schütze
Spectroscopy the bugbear for medical students and technicians: Asked by biologists or clinicians what exactly we are doing at CellTool® we originally answered, that we are developing a unique spectroscopic microscope system that enables easy cell analysis based on Raman spectroscopy. The two “non-words” in the world of biomedical scientists namely spectroscopy and Raman immediately caused to raise hackles and one could see how interest vanished....
 A new application for microscopyNon-invasive cancer diagnosis - von Dr Leo Habets
Cancer has been a part of human life from our earliest days. In research conducted by Aachen-based oncologist Dr Leo Habets, a non-invasive, microscope-based diagnostic procedure has the potential to revolutionise research and progress in understanding the circumstances of the disease, so as to develop new therapeutic approaches. Microscope-based high-content screening systems in basic clinical research: can a non-invasive procedure replace the...
 A new application for microscopyNon-Invasive Cancer Diagnosis - von Dr Leo Habets
Cancer has been a part of human life from our earliest days. In research conducted by Aachen-based oncologist Dr Leo Habets, a non-invasive, microscope-based diagnostic procedure has the potential to revolutionise research and progress in understanding the circumstances of the disease, so as to develop new therapeutic approaches. Microscope-based high-content screening systems in basic clinical research: can a non-invasive procedure replace the...
 |
|